
Over the next few years, cloud computing will continue to evolve from being an innovation facilitator to a business disruptor and, ultimately, a business necessity according to Gartner, Inc.
The “cloud” isn’t floating in the sky, it’s powerful remote servers you access over the internet, giving you flexibility and easy scalability beyond traditional computers.
But this accessibility also opens doors for cyber threats. Protecting the cloud is complex because it’s constantly changing, and attackers exploit hidden gaps, especially as businesses use multiple cloud providers.
Managing cloud risks means knowing where attackers focus most and building a strong program that helps SecOps and DevOps teams work together smoothly. Today, cloud security isn’t just a separate focus, it’s embedded everywhere, protecting not only the cloud but also the AI and apps running within it. This shift shows that security is becoming a shared responsibility across all teams.
Cloud security is the practice of protecting data, systems, and operations in cloud environments, mainly the public cloud. It focuses on securing both the cloud platform itself and everything built inside it but doesn’t include security tools delivered from thecloud to protect external systems.
Cloud providers work hard to secure their platforms, but customers also play a key role. Providers protect the cloud infrastructure, but customers must secure their data, access controls, and how they use the service.
Responsibilities vary by cloud type:
Within all types of public cloud services, customers are responsible for securing their data and controlling who can access that data.
Storing data in the public cloud, managed by third parties and accessed over the internet, creates unique security challenges:
Have you ever wondered how many cloud misconfigurations go unnoticed in your organization? A simple overlooked setting could open the door to attackers without any malware involved.
When it comes to cloud security, organizations face two core challenges:
Visibility: Understanding Your Cloud Environment
Control: Protecting Your Cloud Data and Access
Once you gain clear visibility into your cloud environment, the next essential step is control setting policies and safeguards to protect data and manage who can do what.
As cloud environments grow more complex, visibility and control must extend across the entire application lifecycle — from development to deployment and runtime.
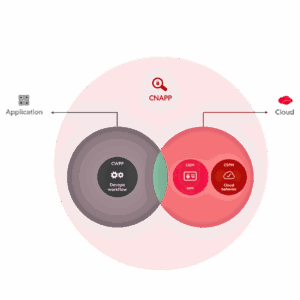
This is where CNAPP comes in. It offers a unified solution that brings together:
Together, they provide full-spectrum protection for your IaaS, PaaS, and cloud-native applications all in one integrated platform.
To stay compliant and reduce regulatory risk:
Cloud is no longer just an IT choice, it’s critical for business success. As companies invest more in cloud technology, securing that cloud becomes vital to protect data, manage risks, and support innovation like AI and automation. The winners will be those who secure their cloud well and embrace it as a core part of their strategy.
Get ready: Cloud isn’t the future anymore, it’s the foundation.